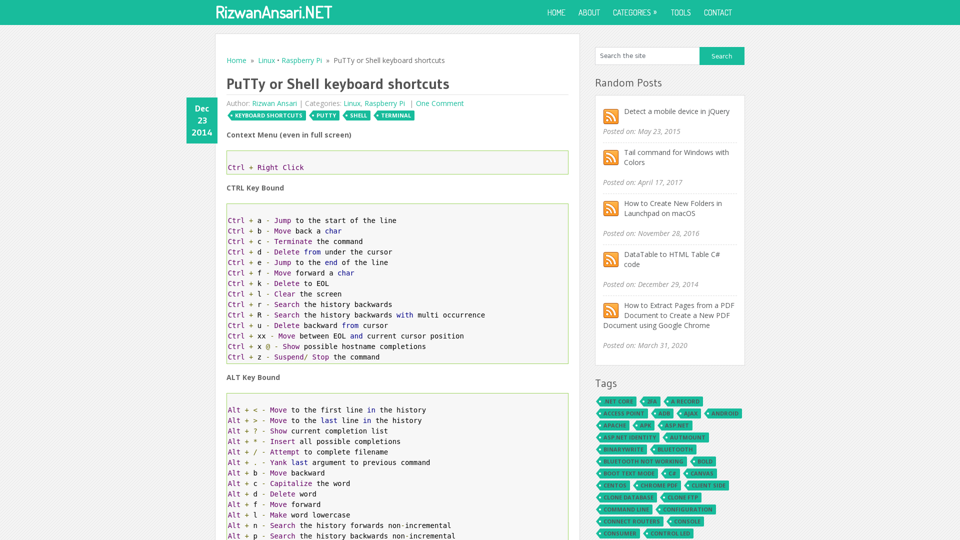
Ctrl Key Bound
- Ctrl + a: Jump to the start of the line
- Ctrl + b: Move back a char
- Ctrl + c: Terminate the command
- Ctrl + d: Delete from under the cursor
- Ctrl + e: Jump to the end of the line
- Ctrl + f: Move forward a char
- Ctrl + k: Delete to EOL
- Ctrl + l: Clear the screen
- Ctrl + r: Search the history backwards
- Ctrl + R: Search the history backwards with multi occurrence
- Ctrl + u: Delete backward from cursor
- Ctrl + xx: Move between EOL and current cursor position
- Ctrl + x @: Show possible hostname completions
- Ctrl + z: Suspend/ Stop the command
Alt Key Bound
- Alt + <: Move to the first line in the history
- Alt + >: Move to the last line in the history
- Alt + ?: Show current completion list
- Alt + *: Insert all possible completions
- Alt + /: Attempt to complete filename
- Alt + .: Yank last argument to previous command
- Alt + b: Move backward
- Alt + c: Capitalize the word
- Alt + d: Delete word
- Alt + f: Move forward
- Alt + l: Make word lowercase
- Alt + n: Search the history forwards non-incremental
- Alt + p: Search the history backwards non-incremental
- Alt + r: Recall command
- Alt + t: Move words around
- Alt + u: Make word uppercase
- Alt + back-space: Delete backward from cursor
These shortcuts can help users navigate and interact with the command-line interface more efficiently, saving time and improving productivity.